We would like to let you know that the Ocean Carbon Data System (OCADS) at NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) published two new data publications. NDP-098 is a data synthesis product containing "A comprehensive global oceanic dataset of discrete measurements of helium isotope and tritium during the hygrographic cruises on various ships from 1952-10-21 to 2016-01-22 (NCEI Accession 0176626)." NDP-099 is a new data numeric package describing "Current calcite (CaCO3) dissolution at the seafloor caused by anthropogenic CO2 (NCEI Accession 0176672)."
NDP-098
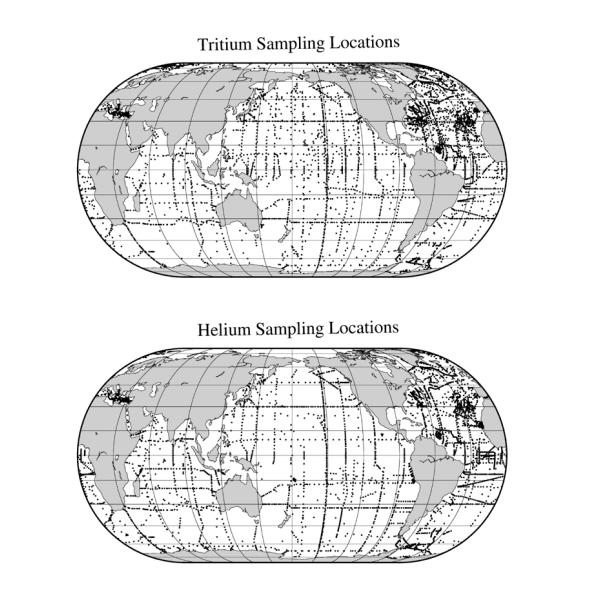
The NDP-098 consists of global oceanic database of tritium and helium isotope measurements made by numerous researchers and laboratories over a period exceeding 60 years: from 1952-10-21 to 2016-01-22 in the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern Ocean, Arctic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, Baltic Sea, Black Sea. Tritium and helium isotope data provide key information on ocean circulation, ventilation, and mixing, as well as the rates of biogeochemical processes, and deep-ocean hydrothermal processes. The dataset includes approximately 60,000 valid tritium measurements, 63,000 valid helium isotope determinations, 57,000 dissolved helium concentrations, and 34,000 dissolved neon concentrations. Some quality control has been applied in that questionable data have been flagged and clearly compromised data excluded entirely. Appropriate metadata has been included: geographic location, date, and sample depth. When available, water temperature, salinity, and dissolved oxygen were included. Data quality flags and data originator information (including methodology) are also included.
This is version 1.1 of NDP-098 prepared by William J. Jenkins, Scott C. Doney et al. The product can be accessed from: https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/ocads/oceans/ndp_098/ndp098.html. Data are available at https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/ocads/data/0176626.xml.
Further details will be described in a paper by Jenkins et al. (2018) submitted to Earth System Science Data (ESSD).
NDP-099
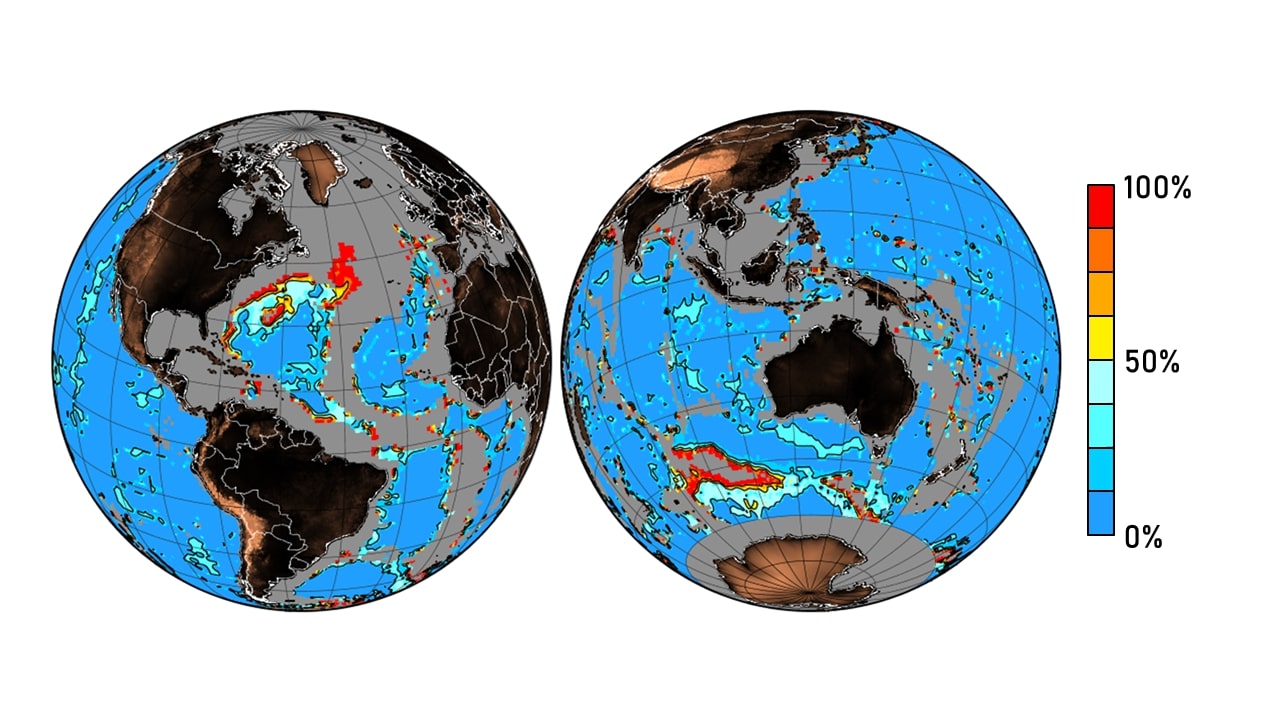
This NCEI accession consists of current CaCO3 dissolution at the seafloor caused by anthropogenic CO2 in the World Oceans. This dataset contains the main results from Sulpis et al. (PNAS, 2018). All the variables have a 1x1 degree resolution. It can be used to compute calcite dissolution at the seafloor for changing bottom-water chemistry, calcite rain rates or current speeds, for instance. Oceanic uptake of anthropogenic CO2 leads to decreased pH, carbonate ion concentration, and saturation state with respect to CaCO3 minerals, causing increased dissolution of these minerals at the deep seafloor. This additional dissolution will figure prominently in the neutralization of man-made CO2. Yet, there has been no concerted assessment of the current extent of anthropogenic CaCO3 dissolution at the deep seafloor. Here, recent databases of bottom-water chemistry, benthic currents, and CaCO3 content of deep-sea sediments are combined with a new rate model to derive the global distribution of benthic calcite dissolution rates and obtain primary confirmation of an anthropogenic component. By comparing pre-industrial with present-day rates, we determine that significant anthropogenic dissolution now occurs in the western North Atlantic, amounting to 40-100% of the total seafloor dissolution at its most intense locations. At these locations, the calcite compensation depth has risen ~300 m. Increased benthic dissolution was also revealed at various hot spots in the southern extent of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. Our findings place constraints on future predictions of ocean acidification, are consequential to the fate of benthic calcifiers, and indicate that a by-product of human activities is currently altering the geological record of the deep sea.
Further details are in Sulpis, et al. 2018.
Sulpis, Olivier; Boudreau, Bernard P.; Mucci, Alfonso; Jenkins, Chris; Trossman, David S.; Arbic, Brian K.; Key, Robert M. (2018). Current calcite (CaCO3) dissolution at the seafloor caused by anthropogenic CO2 (NCEI Accession 0176672). Version 1.1. NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information Dataset. doi: 10.25921/kbqy-4v05
NDP-099 is available at: https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/ocads/oceans/ndp_099/ndp099.html
The associated NCEI accession 0176672 is:
https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/ocads/data/0176672.xml





 Please wait...
Please wait...